Cost Comparison OEM vs Aftermarket Car Parts

You're standing in your garage, staring at your car with a mixture of frustration and concern. That grinding noise from your brakes isn't going away, and now you're facing the inevitable: it's time to replace some parts. But here comes the big question that plagues every car owner – should you go with Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) parts or save some cash with aftermarket alternatives?
I've been there myself. Last year, my 2015 Toyota Camry needed new brake pads and rotors. The price difference between OEM and aftermarket options was significant enough to make me pause and research thoroughly before making a decision. That experience inspired me to create this comprehensive guide to help you understand the real cost differences – both short and long-term – between OEM and aftermarket car parts.
In this article, we'll break down everything you need to know about the cost comparison between OEM and aftermarket parts, examining specific components, quality considerations, and helping you make informed decisions that won't leave your wallet empty or your car underperforming.
What Are OEM and Aftermarket Parts? Defining the Differences
Before diving into cost comparisons, let's clarify exactly what we're discussing.
OEM Parts: The Factory Standard
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts are manufactured either by your vehicle's manufacturer or by a company that supplies components to the manufacturer. These are identical to the parts that were installed in your vehicle when it rolled off the assembly line.
When you buy OEM parts, you're getting components that were specifically designed for your make and model of vehicle. They come with the manufacturer's branding and are typically sold through dealerships or authorized parts retailers.
Aftermarket Parts: The Alternative Options
Aftermarket parts are any components made by companies other than the original vehicle manufacturer. They're designed to function similarly (or sometimes even better) than OEM parts but are produced by third-party manufacturers.
The aftermarket range is vast – from budget options manufactured by unknown companies to high-performance upgrades made by respected brands in the automotive industry. This variety is what creates both opportunity and confusion for car owners looking to save money while maintaining quality.
The Cost Factor: Breaking Down the Price Differences
Now let's get to the heart of the matter – the cost comparison between OEM and aftermarket parts.
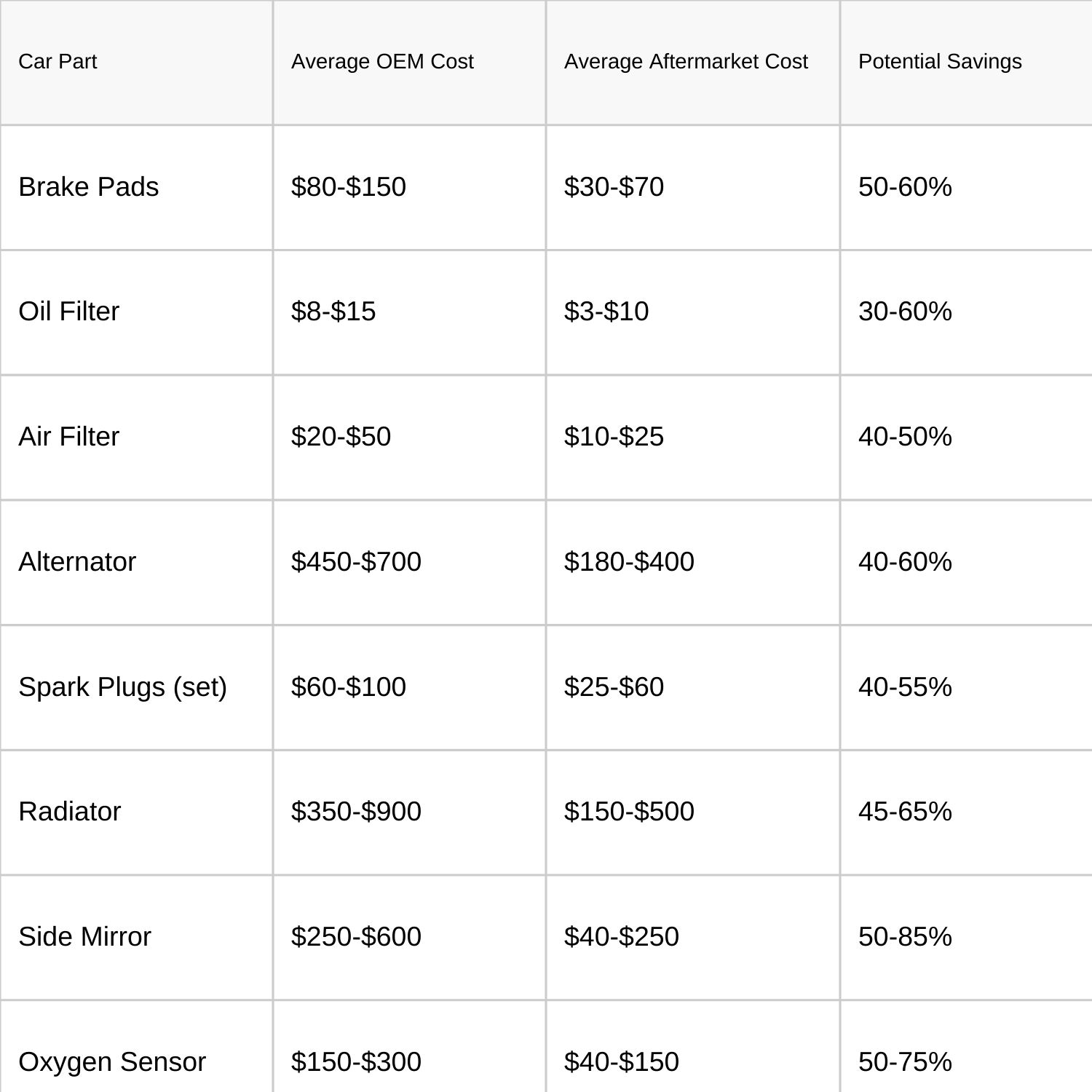
The Price Gap: How Much Can You Actually Save?
According to multiple sources including J.D. Power, OEM parts typically cost about 60% more than their aftermarket counterparts. This price difference can vary widely depending on the specific part and vehicle make, but the trend is consistent across most components.
Let's look at some real-world examples for common replacement parts:
These figures represent industry averages and can vary based on your specific vehicle make, model, and year. For luxury vehicles, the price gap can be even more dramatic.
Why the Price Difference Exists
You might wonder why OEM parts come with such a hefty premium. There are several factors at play:
- Research and Development Costs: Vehicle manufacturers invest heavily in R&D, and these costs are passed on to consumers through parts pricing.
- Quality Control and Testing: OEM parts undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet manufacturer specifications, which adds to production costs.
- Brand Reputation Protection: Manufacturers charge more for parts partly to maintain the perception of superior quality and exclusivity.
- Dealership Markup: When purchasing through dealerships, you're also paying for overhead costs and profit margins.
- Limited Competition: Since OEM parts come from a single source, there's no competitive pricing pressure like there is in the aftermarket space.
From my personal experience, I've found that the biggest aftermarket savings come with body components and non-critical maintenance items. When I needed to replace the side mirror on my car after an unfortunate encounter with a garage wall, the dealership quoted me $425 for the OEM mirror, while I found a high-quality aftermarket version for just $95 – a savings of over 75%!
Quality Comparison: Do You Always Get What You Pay For?
The cost is only part of the equation. The real value comes from understanding the quality differences between OEM and aftermarket parts.
OEM Quality: Consistency and Reliability
OEM parts offer several quality advantages:
- Guaranteed Fit: Since they're identical to the original parts, OEM components will always fit perfectly.
- Consistent Performance: You can expect the same performance as your original part.
- Warranty Protection: Most OEM parts come with a one-year warranty, and using them typically won't void your vehicle's warranty.
- Simplified Selection Process: There's only one OEM option per part, eliminating confusion about which version to buy.
Aftermarket Quality: A Spectrum of Options
The quality of aftermarket parts varies dramatically:
- Budget Aftermarket: The cheapest options may be made with inferior materials and less precise manufacturing processes. These might wear out faster or perform below OEM standards.
- Mid-Range Aftermarket: These parts usually offer good value, with quality close to OEM but at lower prices.
- Premium Aftermarket: Some aftermarket parts from reputable brands actually exceed OEM specifications, using better materials or improved designs to address known weaknesses in original parts.
During my research for brake components, I discovered that certain premium aftermarket brake pad manufacturers actually supply components to major automakers but sell the same or similar formulations under their own brand for less. In these cases, you might be getting essentially the same quality for a fraction of the price.
Part-Specific Analysis: When to Go OEM vs. Aftermarket
Not all car parts are created equal when it comes to the OEM vs. aftermarket decision. Let's break down recommendations for specific components:
Safety-Critical Components
For parts that directly impact safety, the decision becomes more nuanced:
Brake Components: Quality matters tremendously for brakes. While many premium aftermarket brake pads and rotors perform excellently (sometimes better than OEM for specialized uses like performance driving), budget options can compromise stopping distance and fade resistance. A good middle ground is to choose aftermarket products from respected brands like Akebono, Centric, or Wagner.
Airbag Systems: This is one area where OEM is strongly recommended. The precise timing and deployment characteristics of airbags are critical for safety, and variations in aftermarket options could affect performance in accidents.
Suspension Components: For primary suspension components like struts and control arms, mid-to-high range aftermarket parts from companies like Moog, KYB, or Bilstein often provide excellent value and sometimes improved performance over OEM.
Engine and Transmission Parts
The heart of your vehicle deserves careful consideration:
Filters (Oil, Air, Fuel): Good quality aftermarket filters from brands like Wix, Mann, or Bosch often match or exceed OEM specifications at lower prices. However, extremely cheap filters may not provide adequate protection.
Major Components (Alternators, Starters, Water Pumps): Remanufactured OEM or quality aftermarket options from established brands typically offer the best value. These parts are rebuilt using the original core with new wear components.
Engine Control Modules and Sensors: Electronic components are an area where OEM often justifies the extra cost due to more consistent performance and fewer compatibility issues.
Body and Appearance Parts
For components that affect your vehicle's appearance:
Body Panels: Aftermarket body panels can vary widely in fit and finish. For vehicles less than 5 years old, OEM panels ensure perfect color matching and fitment. For older vehicles, quality aftermarket panels can save significant money.
Lights and Mirrors: Aftermarket lighting can be hit-or-miss. While some options are virtually indistinguishable from OEM, others may have poor seals leading to moisture intrusion or different light patterns. Research specific brands before purchasing.
Interior Components: For visible interior parts, OEM often provides better color matching and fit, but the price premium may be substantial. The decision often comes down to how noticeable the part will be inside your vehicle.
The Hidden Costs: Looking Beyond the Price Tag
When comparing OEM and aftermarket parts, there are several indirect costs to consider:
Installation Time and Labor Costs
Sometimes aftermarket parts may not fit as perfectly as OEM components, leading to increased installation time and higher labor costs. What you save on the part might be lost in additional labor charges.
For example, when replacing my car's serpentine belt tensioner, the aftermarket part required slight modifications to fit correctly, adding about 30 minutes to the repair time. If I had been paying a mechanic by the hour, this would have eaten into my savings.
Lifespan and Durability
While initial costs matter, the total cost of ownership depends on how long the part lasts. A cheaper aftermarket part that fails in half the time of an OEM component might end up costing more in the long run.
Based on consumer surveys and mechanic feedback, aftermarket parts typically fall into these durability categories compared to OEM:
- Budget aftermarket: 50-70% of OEM lifespan
- Mid-range aftermarket: 70-100% of OEM lifespan
- Premium aftermarket: 90-120% of OEM lifespan
Warranty Considerations
OEM parts typically come with a one-year warranty. Aftermarket warranties vary dramatically:
- Some offer limited 90-day warranties
- Others match the OEM one-year standard
- Premium brands might offer lifetime warranties on certain components
Additionally, using aftermarket parts could potentially affect your vehicle warranty in specific situations, though the Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act protects consumers from blanket warranty denials based solely on aftermarket part usage.
Real-World Scenarios: When to Choose OEM vs. Aftermarket
Let's explore some common scenarios and provide recommendations:
Scenario 1: Daily Driver with 100,000+ Miles
For a higher-mileage vehicle that you plan to keep for several more years, aftermarket parts often make the most sense for routine maintenance items. The cost savings are significant, and the potential slight reduction in lifespan is less consequential given the vehicle's age.
Recommended approach: Choose mid-range to premium aftermarket parts for most maintenance components, reserving OEM purchases for critical electronic modules or parts where precise fit is essential.
Scenario 2: Newer Vehicle Under Warranty
For vehicles still under manufacturer warranty, using OEM parts for major components helps avoid potential warranty complications.
Recommended approach: Use OEM for major engine, transmission, and electronic components. Consider quality aftermarket options for routine maintenance items like filters, brake pads, and spark plugs.
Scenario 3: Luxury or Performance Vehicle
High-end vehicles often have more specialized components where aftermarket options might not deliver the same driving experience.
Recommended approach: Stick with OEM for components that affect driving dynamics and performance. Look for high-end aftermarket options from respected brands for maintenance items. In some cases, performance-focused aftermarket parts may actually improve upon OEM specifications.
Scenario 4: Classic Car Restoration
For older vehicles being restored, a mixed approach typically works best.
Recommended approach: Use OEM or high-quality reproduction parts for visible components and unique systems. Aftermarket options make sense for standard wear items and mechanical components where modern materials might actually improve reliability.
Making Smart Decisions: How to Choose Quality Aftermarket Parts
If you decide to go the aftermarket route, here are some strategies to ensure you're getting quality parts:
Research the Brand Reputation
Not all aftermarket brands are created equal. Companies like Bosch, Denso, Moog, and Bilstein have established reputations for quality comparable to or exceeding OEM specifications. Online reviews, automotive forums, and professional mechanic recommendations can help identify trusted brands.
Check for Certifications
Look for aftermarket parts with industry certifications like:
- CAPA (Certified Automotive Parts Association) for body parts
- DOT certification for lights and safety equipment
- ISO certification for manufacturing quality
Compare Material Specifications
When possible, compare the materials used in aftermarket parts to OEM specifications. Some premium aftermarket companies actually improve upon OEM designs by using better materials or addressing known failure points.
Consider the Source
Purchase aftermarket parts from reputable retailers who stand behind their products. Many auto parts stores offer their own warranty programs on top of manufacturer warranties.
The Final Analysis: Balancing Cost and Quality
After analyzing hundreds of parts across multiple vehicle makes and models, here's a simplified decision framework:
When OEM Makes More Sense:
- Complex electronic components: Engine control modules, advanced sensors, and complex integrated systems.
- Collision repair parts: When proper fit and finish are critical.
- Rare or vehicle-specific components: Parts unique to your vehicle with limited aftermarket support.
- Warranty-covered vehicles: To avoid potential complications with warranty claims.
- When perfect appearance matters: Visible components where exact color matching and fit are important.
When Aftermarket Makes More Sense:
- Routine maintenance items: Filters, brake pads, spark plugs, and other regularly replaced parts.
- Well-established parts: Components with many aftermarket options from reputable brands.
- Older vehicles: Cars beyond warranty where cost savings outweigh minor fit or performance differences.
- Performance upgrades: When seeking improved performance beyond OEM specifications.
- Budget constraints: When cost is a primary concern and quality aftermarket options exist.
Conclusion: Finding Your Personal Balance
The OEM versus aftermarket decision ultimately comes down to your specific situation, priorities, and vehicle needs. By understanding the true cost differences – both immediate price and long-term value – you can make informed choices that keep your vehicle running reliably without unnecessary expense.
From my experience maintaining multiple vehicles over the years, I've found that a balanced approach works best. I use OEM parts for critical systems and electronic components, while choosing quality aftermarket options for routine maintenance items and mechanical parts where the savings are substantial and performance differences minimal.
Remember that the cheapest option isn't always the most economical in the long run. Consider the total cost of ownership, including durability, warranty protection, and potential impacts on other vehicle systems.
What's your experience with OEM and aftermarket parts? Have you found certain brands or components where aftermarket options actually outperform the originals? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!


